Describe the Relationship of the Immune System to Organ Transplants
The white blood cells are a key component. The immune system is a large complex network of mobile interactive cells and molecules that circulate through the bodys lymph and blood vessels tissues and organs to protect it from.
Thus in organ transplantation much attention has been paid to this HLA-epitope matching as a topic of interest beyond serological MHC matching.
. The lymphatic system is the system of vessels cells and organs that carries excess fluids to the bloodstream and filters pathogens from the blood. In the case of organ transplants the greatest challengeafter locating an organ that is appropriate for transplantationis to keep the new organ healthy by preventing rejection. How the immune system can make getting an organ transplant trickier.
In your answer be sure to. Way the immune system is involved in the rejection of transplanted organs 1 the immune system sees the new organ like a disease and tries to kill it. Even so almost all recipients eventually lose their transplant.
Organ transplants work much like a pathogen. Historically the presence of donor-specific antibodies DSA that recognize donor HLA molecules incompatible ABO blood group. HLAMatchmaker provides information about the reactivity of anti-HLA antibodies at the epitope level 124125.
Helping the immune system accept transplanted organs. If waiting for an organ transplant werent difficult enough some patients are forced to wait longer than others because of something called sensitization Dr. The lymphatic system for most people is associated with the immune system to such a degree that the two systems are virtually indistinguishable.
The new organ makes different chemicals that our organs so the body tries to fight off and kill the new organ the same way it would a pathogen triggers an immune response. Andrew Bentall a Mayo Clinic transplant nephrologist explains how the bodys immune. Antigens which possess the same epitope are referred to as cross-reacting groups CREGs.
Here we explain how it works and the cells organs. There are two main arms of immune response. Because the bone marrow cells being transplanted contain lymphocytes capable of mounting an immune response and because the recipients immune response has been destroyed before receiving the transplant the donor cells may attack the recipient tissues causing graft-versus-host disease.
Symptoms of this disease which usually include a rash and damage to the liver. Traditionally when an individual undergoes a transplant operation they also have to undergo drug therapy to suppress the activity of the immune system and to prevent rejection of the new organ. The Immune System and Organ Rejection.
However despite major improvements in graft survival initially rejection of the donor tissue often occurs with time. Causes Your bodys immune system usually protects you from substances that may be harmful such as germs poisons and sometimes cancer cells. Transplant or graft.
Describe the structure and function of the primary and secondary lymphatic organs. Discuss the cells of the immune system how they function and their relationship with the lymphatic system. Describe the relationship of the immune system to organ transplants and the use of immunosuppressant drugs to prevent the rejection of a transplanted organ.
Discuss the role of the immune response in transplantation and cancer Describe the interaction of the immune and lymphatic systems with other body systems In June 1981 the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC in Atlanta Georgia published a report of an unusual cluster of five patients in Los Angeles California. The immune system is the complex collection of cells and organs that destroys or neutralizes pathogens that would otherwise cause disease or death. That is typically done with medication or many medications that help trick the body into recognizing other as self.
However the humoral immune system also provides a significant barrier to solid organ transplantation due to the antibody-mediated recognition of non-self proteins and carbohydrates expressed on transplanted organs. Artificial organs such as artificial bone can be implanted successfully because such organs prostheses do not produce antigenic substances. However during organ transplantation the immune system also attacks transplanted organs and leads to immune rejection and transplantation failure.
Currently people receiving organ transplants must take drugs to suppress the inflammatory immune response that leads to rejection. The immune system recognizes and attacks non-self antigens making up the cornerstone of immunity activity against infection. Humoral using antibodies and cellular using immune cells.
Severe immune-mediated transfusion reactions usually involve the humoral arm. The immune system defends our body against invaders such as viruses bacteria and foreign bodies. Mayo Clinic Minute.
Introducing an organ from a donor into a recipient almost always leads to the recipients immune system recognising the new organ as foreign and mounting an immune response. Transplant rejection is a process in which a transplant recipients immune system attacks the transplanted organ or tissue. Every organ transplant recipient owes his or her life to drugs that muzzle the immune system and prevent it from destroying.
Organ transplantation is the surgical replacement of diseased organs with healthy organs grafts from live or cadaver donors. In the case of a foreign red blood cell antigen the patients pre-existing antibodies bind to the antigen coating the donor RBCs. Bone-marrow transplants effectively bring their own immune system with them often rejecting the new host instead of the other way around in a reaction known as graft-versus-host disease.
The swelling of lymph nodes during an infection and the transport of lymphocytes.

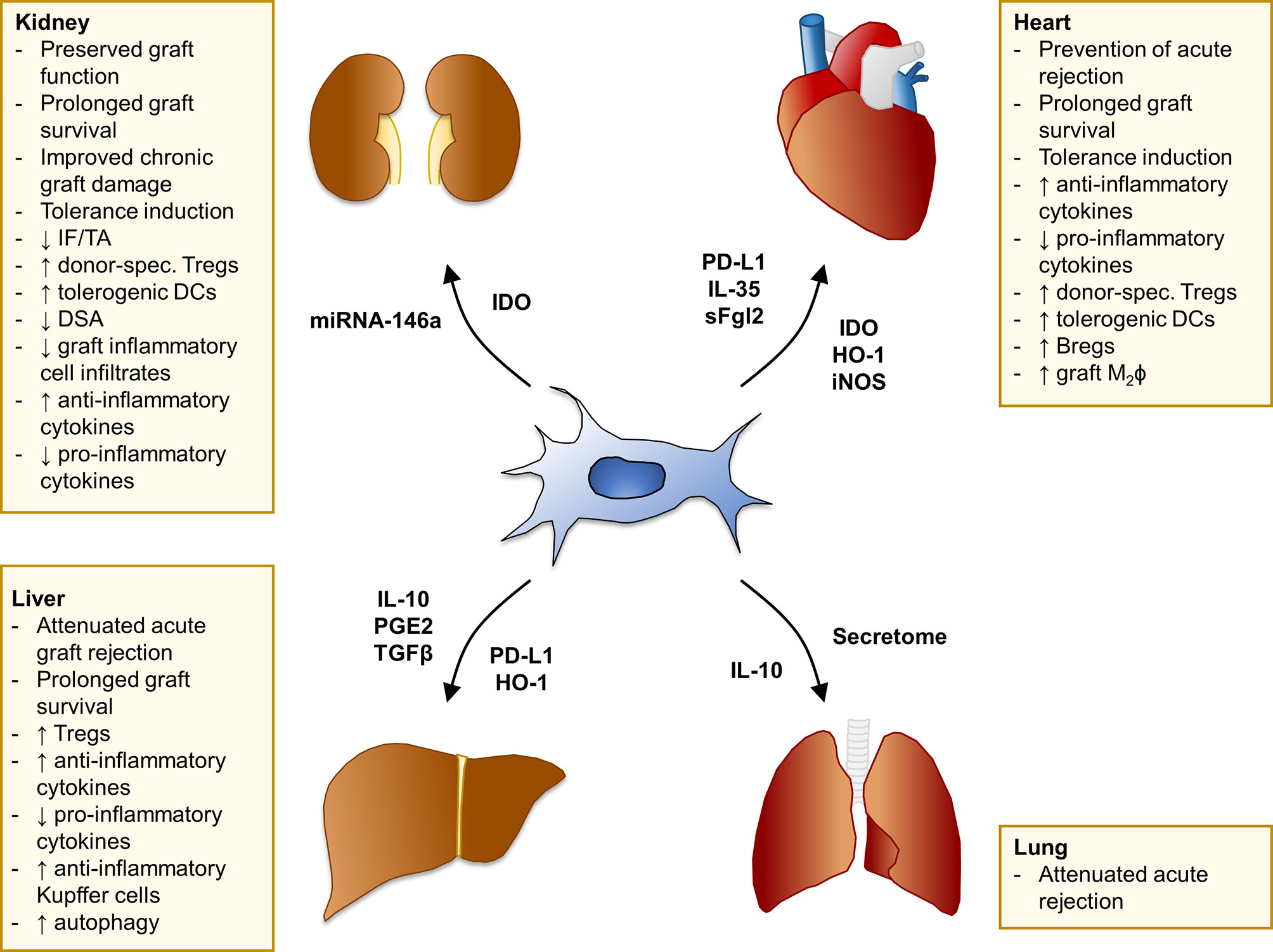
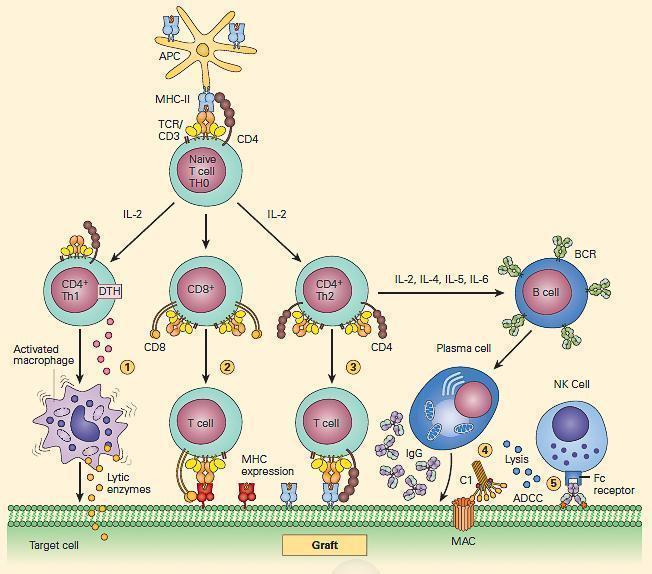
Transplantation Immune Responses Immunopaedia
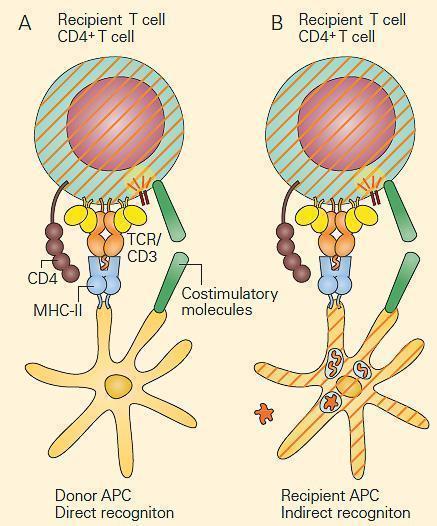
Transplantation Immune Responses Immunopaedia

Session 9 The Immunology Of Organ Transplantation Ibiology

The Immunology Of Organ Transplantation Surgery Oxford International Edition

Frontiers Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy In Solid Organ Transplantation Immunology

Trials And Tribulations Of A Transplant Science In The News



No comments for "Describe the Relationship of the Immune System to Organ Transplants"
Post a Comment